Pulp stone
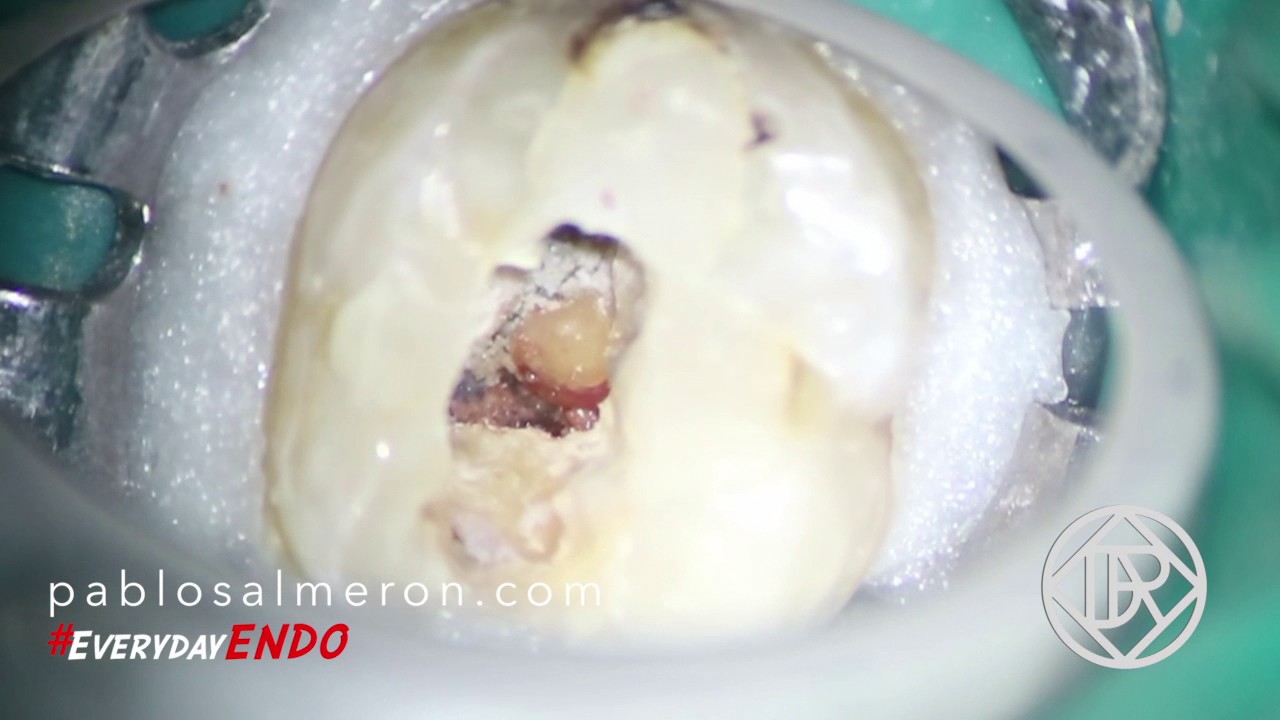
In this case, I found a pulp stone inside of a mandibular second molar. Dental pulp tissue can form dentin or osteodentin in the reaction to the homeostasis induced either by surgical or chemical stimulation, and the activity of pulp cells regulates the calcification of pulp tissue.
Pulp stones are calcified bodies in the dental pulps of the teeth, which can be seen in the pulps of healthy, diseased, and even un-erupted teeth in the primary and permanent dentition. Dental pulp stones may be free, attached, or embedded in the coronal or radicular pulp. They are considerably more common in the pulp chamber than in the root canal and may occur in a single tooth or several teeth.
Although pulp stones have no clinical significance, they lead to complications when endodontic therapy is needed.
As you can see in the video, their large size in pulp chamber may block access to canal orifices and alter the internal anatomy, and attached stones may deflect or engage the tip of exploring instruments, preventing their easy passage down the canal. In this kind of situation the use of the surgical microscope is mandatory.
This video has been done with a Labomed Magna microscope and Canon EOS camera.
“You can only treat what you can see”.
PhD. MSc. Dr. Pablo Salmeron.

